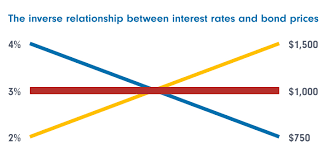
Relationship between bonds and interest
Bonds and interest rates have an inverse relationship, meaning that as interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, and vice versa.
When interest rates rise, new bonds are issued with higher interest rates, making them more attractive to investors. As a result, the demand for existing bonds with lower interest rates decreases, causing their prices to fall. Conversely, when interest rates fall, new bonds are issued with lower interest rates, making existing bonds with higher interest rates more attractive to investors. This increases the demand for existing bonds, causing their prices to rise.
The relationship between bonds and interest rates is based on the concept of opportunity cost. Opportunity cost refers to the cost of choosing one investment over another. When interest rates rise, the opportunity cost of holding a bond with a lower interest rate increases because investors could earn a higher return by investing in a new bond with a higher interest rate. This reduces the demand for existing bonds, causing their prices to fall.
On the other hand, when interest rates fall, the opportunity cost of holding a bond with a higher interest rate increases because investors could earn a lower return by investing in a new bond with a lower interest rate. This increases the demand for existing bonds, causing their prices to rise.
It’s important to note that the relationship between bonds and interest rates is not always linear and can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as inflation expectations, credit risk, and market sentiment. Therefore, it is important for investors to consider a variety of factors when making investment decisions.
When the economy is bad, is it generally better to invest in stocks or bonds?
When the economy is bad, it is generally better to invest in bonds than stocks. This is because bonds are generally considered to be less risky than stocks and offer a more stable source of income. 채권 금리 상관관계
During an economic downturn, stock prices can be volatile and unpredictable as companies face declining revenues and earnings. This can make it difficult for investors to accurately predict future stock performance and can result in significant losses. In contrast, bonds offer a fixed rate of return and are generally less affected by short-term market fluctuations.
In addition, during a bad economy, interest rates tend to fall as central banks attempt to stimulate economic growth. This can be beneficial for bond investors, as bond prices tend to rise as interest rates fall. This is because as interest rates fall, new bonds are issued with lower interest rates, making existing bonds with higher interest rates more attractive to investors. This increases the demand for existing bonds, causing their prices to rise.
However, it’s important to note that not all bonds are created equal, and some may be more risky than others. High-yield bonds, also known as junk bonds, offer higher interest rates but also come with a higher risk of default. Therefore, it is important for investors to carefully evaluate the credit risk of the bonds they are considering investing in.
Overall, during a bad economy, it may be beneficial for investors to allocate a portion of their portfolio to bonds to help mitigate risk and provide a stable source of income. However, it’s important to consult with a financial advisor and conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.